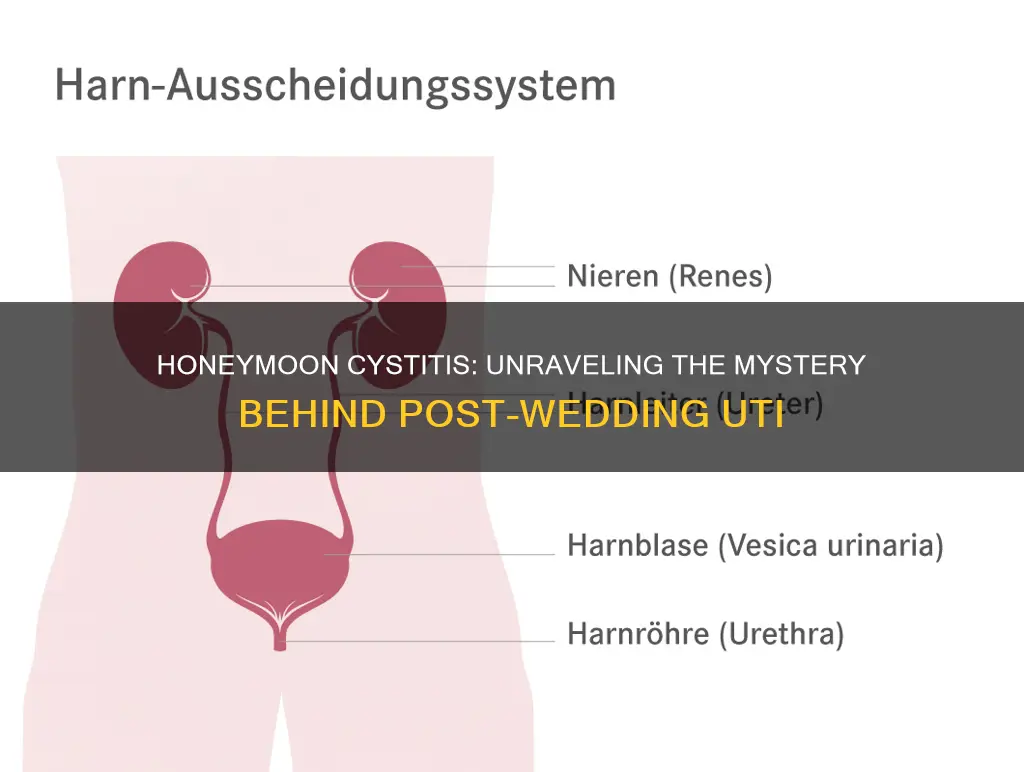
Honeymoon cystitis, also known as post-nuptial cystitis, is a common phenomenon where women experience symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI) shortly after their wedding night. This condition often arises due to several factors, including increased sexual activity, changes in diet, and the physical stress of the wedding day. The act of intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, especially if proper hygiene practices are not followed. Additionally, the consumption of certain foods and drinks, such as spicy dishes, alcohol, and caffeine, can irritate the urinary tract and increase the risk of infection. The physical and emotional stress of the wedding day can also weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to UTIs. Understanding these factors can help couples take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of developing honeymoon cystitis.
What You'll Learn
- Romantic Getaway: Urinary tract infection risk increases during intimate activities
- Stress and Hormones: Hormonal changes during intimacy may irritate the bladder
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can lead to cystitis after sex
- Bacterial Overgrowth: Certain bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, increasing infection risk
- Immune System: Reduced immune function during travel may contribute to cystitis

Romantic Getaway: Urinary tract infection risk increases during intimate activities
The idea of a romantic getaway is often associated with relaxation, pleasure, and intimacy. However, for some individuals, this idyllic scenario can inadvertently lead to an unpleasant experience: a urinary tract infection (UTI). The phenomenon of "honeymoon cystitis," a term sometimes used to describe UTIs that occur during or shortly after sexual activity, is a concern for many couples. Understanding the reasons behind this occurrence is essential for couples to take preventive measures and ensure a healthy and enjoyable intimate experience.
During intimate activities, several factors can contribute to the development of UTIs. Firstly, the introduction of new bacteria into the urinary tract is a significant risk factor. Sexual intercourse can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina and urethra, allowing pathogenic bacteria to enter the urinary tract more easily. Certain sexual positions and activities can also increase the likelihood of bacterial transmission, especially if one or both partners have an existing UTI or a history of recurrent infections.
The physical act of sexual intercourse can also cause mechanical irritation and trauma to the urinary tract. The pressure exerted during penetration can lead to minor injuries or inflammation, making the tract more susceptible to bacterial invasion. Additionally, the flow of urine during sexual arousal and orgasm may not always be as efficient as during normal urination, allowing bacteria to linger and potentially multiply.
Certain lifestyle factors and behaviors can further exacerbate the risk of developing honeymoon cystitis. For instance, dehydration is a common trigger for UTIs. Engaging in intimate activities without adequate fluid intake can reduce urine production, concentrating bacteria and making it more challenging for the body to flush out pathogens. Similarly, a lack of sleep and fatigue can weaken the immune system, making it less effective at fighting off potential infections.
To mitigate the risk of UTIs during romantic getaways, couples can take several proactive measures. Ensuring proper hydration before and after intimate activities is crucial. Drinking plenty of water can help maintain a healthy urinary flow and dilute the concentration of bacteria in the urinary tract. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, including regular cleansing of the genital area, can reduce the introduction of harmful bacteria. Using condoms can also provide a physical barrier, minimizing the risk of bacterial transmission.
In conclusion, while a romantic getaway should be a time of joy and intimacy, it is essential to be aware of the potential risks associated with UTIs. By understanding the factors that contribute to honeymoon cystitis, couples can take simple yet effective precautions. These may include maintaining hydration, practicing good hygiene, and considering the use of protective measures to ensure a healthy and memorable intimate experience. Being informed and proactive can help couples enjoy their romantic escape without the added worry of a UTI.
Honeymoon Blues: When to Call Off the Trip
You may want to see also

Stress and Hormones: Hormonal changes during intimacy may irritate the bladder
The phenomenon of "honeymoon cystitis," a term often used to describe the occurrence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) following sexual activity, has intrigued researchers and medical professionals for years. While the exact reasons behind this occurrence are still being studied, one significant factor that has emerged is the role of stress and hormonal changes during intimate moments.
During intimate encounters, the body undergoes a series of physiological changes. The release of hormones, such as oxytocin, plays a crucial role in the sexual response cycle. Oxytocin is often referred to as the "love hormone" as it is associated with feelings of bonding, pleasure, and relaxation. However, this hormone also has a direct impact on the urinary system. As oxytocin levels rise, it can cause the bladder to become more sensitive and irritable. This heightened sensitivity can lead to a variety of symptoms, including a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and even pain in the lower abdomen.
The hormonal changes that occur during intimacy can also affect the immune system's response. When the body is in a state of arousal and relaxation, it may become more susceptible to bacterial invasion. Certain bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), are commonly found in the intestines and can sometimes travel to the bladder during sexual activity, especially if proper hygiene practices are not followed. These bacteria can then multiply rapidly in the bladder, leading to a UTI.
Additionally, the act of intercourse can introduce bacteria from the partner's genital area into the urethra, further increasing the risk of infection. The urethra, being a relatively short and narrow passage, provides an ideal environment for bacteria to multiply quickly. This is especially true if the individual is already predisposed to UTIs or has a weakened immune system.
Managing stress and understanding the hormonal changes that occur during intimacy can be essential in preventing honeymoon cystitis. Practicing good hygiene, including proper cleaning before and after sexual activity, can also reduce the risk of bacterial transmission. It is also beneficial to stay well-hydrated, as this can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. For those prone to UTIs, consulting a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options is recommended.
Marriott Stellaris vs. Ritz-Carlton Aruba: The Ultimate Honeymoon Showdown
You may want to see also

Dehydration: Not drinking enough fluids can lead to cystitis after sex
Dehydration is a common factor that can contribute to the development of cystitis, especially after sexual intercourse. When you engage in physical activity, particularly during sex, your body's fluid levels can become depleted. This is because sexual activity can cause increased sweating and a rise in body temperature, leading to fluid loss. Additionally, the act of sex itself can be physically demanding, requiring a significant amount of energy and potentially causing you to breathe heavily, which can also contribute to fluid loss.
After sexual activity, it is essential to rehydrate your body to maintain optimal health and reduce the risk of cystitis. Drinking enough fluids, especially water, is crucial to replenish the lost fluids and maintain the body's hydration levels. When you are dehydrated, the concentration of substances in your urine increases, making it more concentrated and potentially more irritable to the bladder lining. This can lead to inflammation and discomfort, which are common symptoms of cystitis.
The impact of dehydration on cystitis is particularly relevant during the 'honeymoon phase' of sexual activity, where couples may engage in more frequent intimate moments. In this period, the body's fluid requirements are higher, and the risk of dehydration is increased. It is essential to be mindful of this and take proactive steps to stay hydrated. Simple measures such as carrying a water bottle during intimate moments and ensuring easy access to fluids can help prevent dehydration and reduce the likelihood of developing cystitis.
To avoid dehydration, it is recommended to drink water regularly throughout the day, even if you don't feel particularly thirsty. This is especially important before, during, and after sexual activity. By staying well-hydrated, you can help maintain the body's natural balance and reduce the chances of cystitis occurring. Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet rich in fluids can also contribute to overall hydration and support bladder health.
In summary, dehydration is a significant factor that can contribute to the development of cystitis after sex. By understanding the impact of fluid loss during sexual activity and taking proactive steps to rehydrate, individuals can reduce the risk of cystitis and promote overall bladder health. Staying informed and implementing simple hydration practices can make a significant difference in preventing this common issue.
Dive into Adventure: Swimming at Honeymoon Island
You may want to see also

Bacterial Overgrowth: Certain bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, increasing infection risk
Bacterial overgrowth is a common issue that can lead to various health problems, and it plays a significant role in the development of honeymoon cystitis, a condition often experienced by newlywed couples. This phenomenon is not merely a myth but a real medical condition with a scientific basis. The term "honeymoon cystitis" is used to describe the sudden onset of urinary tract infections (UTIs) that some individuals experience shortly after their wedding day. While it may seem romantic, the underlying cause is quite intriguing and worth understanding.
The human body is home to countless microorganisms, including bacteria, which naturally reside in various areas, such as the skin, intestines, and genitals. In a healthy individual, these bacteria coexist peacefully, often providing benefits like aiding digestion. However, certain conditions can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to bacterial overgrowth. One such condition is the creation of a warm and moist environment, which certain bacteria find ideal for their survival and proliferation.
Warm and moist environments, such as those found in the genital area, provide the perfect breeding ground for specific bacteria. These bacteria, including certain strains of Escherichia coli (E. coli), can multiply rapidly, leading to an overabundance of microorganisms in the urinary tract. The result is an increased risk of infection, as the body's natural defenses may struggle to keep up with the sudden surge in bacterial population. This is particularly concerning for the urinary tract, which is already susceptible to infections due to its structure and function.
Honeymoon cystitis often occurs when the body's natural barriers and immune responses are momentarily overwhelmed by the sudden influx of bacteria. The warm and moist conditions created by the honeymoon period, including increased physical intimacy and potential changes in hygiene routines, can contribute to this bacterial overgrowth. It is essential to recognize that this is not a reflection of the quality of the relationship or the honeymoon itself but rather a biological response to specific environmental factors.
Understanding the role of bacterial overgrowth in honeymoon cystitis can help individuals take preventive measures. Maintaining good hygiene practices, staying hydrated, and ensuring a clean and dry genital area can significantly reduce the risk of developing UTIs. Additionally, consulting with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options is crucial in managing and preventing this condition. By addressing the underlying causes, individuals can enjoy their honeymoon without the worry of unexpected health issues.
Time Tebow's Honeymoon in Albania: A Unique Choice Explored
You may want to see also

Immune System: Reduced immune function during travel may contribute to cystitis
The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and preventing infections. During travel, individuals often experience a temporary reduction in immune function, which can make them more susceptible to various illnesses, including cystitis. This condition, commonly known as honeymoon cystitis, is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that affects many travelers, especially those embarking on romantic getaways or adventurous trips.
When the immune system is compromised, the body's natural defense mechanisms become less effective, allowing pathogens to invade and multiply more easily. In the case of cystitis, the reduced immune response can lead to an overgrowth of bacteria in the urinary tract, resulting in inflammation and infection. This is particularly concerning for travelers as they may encounter new environments, different water sources, and potentially contaminated food, all of which can increase the risk of cystitis.
Several factors contribute to the decreased immune function during travel. Firstly, travel-related stress and fatigue can take a toll on the body's ability to fight off infections. Prolonged periods of travel, especially in crowded and unfamiliar settings, can lead to physical and mental exhaustion, making individuals more vulnerable to illness. Additionally, changes in diet and hydration levels while traveling can impact the immune system. Consuming unfamiliar foods or inadequate fluid intake may disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, further compromising immune function.
Furthermore, the lack of familiarity with the local environment can contribute to the development of cystitis. Travelers may encounter new bacteria or viruses that their bodies are not accustomed to, making it harder for the immune system to recognize and combat these pathogens. This is especially true in regions with limited access to clean water and sanitation facilities, where the risk of waterborne infections increases.
Understanding the relationship between the immune system and cystitis is essential for travelers to take preventive measures. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle during travel, such as getting adequate rest, staying hydrated, and practicing good hygiene, can help support immune function. Additionally, travelers should be cautious about their dietary choices, ensuring they consume nutritious foods and stay away from potential sources of contamination. By being mindful of these factors, travelers can reduce the likelihood of developing honeymoon cystitis and enjoy their journeys with a healthier and more resilient immune system.
The Mysterious Disappearance of Julie: A 1956 Honeymoon Mystery
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Honeymoon cystitis, also known as post-nuptial cystitis, is a term used to describe the occurrence of urinary tract infection (UTI) in women shortly after a wedding or honeymoon. It is a relatively common phenomenon, especially in the first few days to a week after the wedding.
The exact cause of honeymoon cystitis is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its occurrence. One primary reason is the physical and emotional stress of the wedding and honeymoon, which can weaken the immune system. Additionally, the act of sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, leading to infection. The use of spermicides, which can alter the natural pH balance of the vagina, is also thought to play a role.
Yes, the symptoms of honeymoon cystitis are similar to those of a typical urinary tract infection. These may include a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, cloudy or bloody urine, and lower abdominal pain. Some women may also experience fever and chills.
Preventing honeymoon cystitis involves several measures. Staying well-hydrated before and after the wedding can help flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Using non-spermicidal lubricants during intercourse and ensuring good hygiene practices can also reduce the risk. Additionally, women can consider taking probiotics to support a healthy urinary tract microbiome. If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical advice is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.







