The honeymoon phase, a period of improved insulin sensitivity and reduced reliance on medication, is a crucial aspect of managing Type 1 diabetes. However, understanding the duration of this phase can vary significantly among individuals. This paragraph will explore the factors influencing the length of the honeymoon phase and its implications for diabetes management, providing valuable insights for those newly diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes.
What You'll Learn
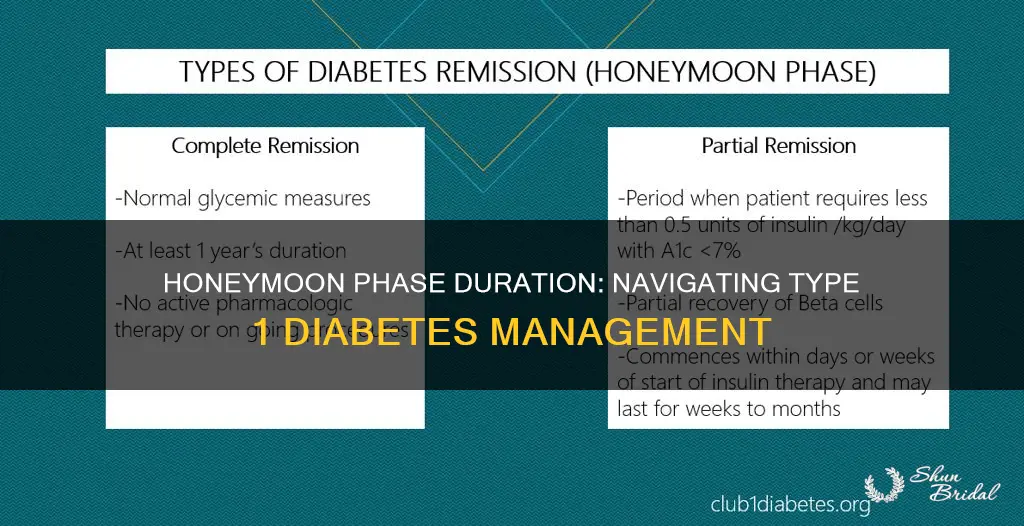
- Duration: The honeymoon phase's length varies, typically lasting 1-5 years post-diagnosis
- Insulin Production: It involves a temporary increase in insulin production by the pancreas
- Blood Sugar Control: Improved blood sugar control is a key characteristic during this period
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, exercise, and stress management can influence honeymoon phase duration
- Individual Variability: Each person's honeymoon phase may differ in length and intensity

Duration: The honeymoon phase's length varies, typically lasting 1-5 years post-diagnosis
The honeymoon phase in Type 1 diabetes refers to a period of time after diagnosis when the body's immune system may still be producing some insulin, leading to improved blood sugar control. This phase can be a crucial period for individuals newly diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes, as it provides an opportunity to manage the condition effectively and potentially delay or reduce the need for insulin injections. However, the duration of this honeymoon phase can vary significantly from person to person.
On average, the honeymoon phase typically lasts for 1 to 5 years following the diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes. During this time, the body's insulin production may gradually decline, but it can still be sufficient to maintain relatively stable blood sugar levels. This period can be a challenging time for patients and healthcare providers alike, as it often involves a delicate balance between managing blood glucose levels and avoiding the complications associated with low insulin production.
Several factors influence the length of the honeymoon phase. Firstly, the individual's overall health and the presence of any other medical conditions can impact the duration. Additionally, the timing and type of diabetes diagnosis play a role. Some studies suggest that a longer honeymoon phase may be observed in individuals who are diagnosed at a younger age or have a more recent onset of symptoms. It is also important to note that the honeymoon phase can vary in intensity, with some people experiencing a more prolonged and milder decline in insulin production, while others may have a shorter but more abrupt drop in insulin levels.
During this phase, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Patients are encouraged to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, to optimize their blood sugar control. Healthcare providers may also adjust the treatment plan, such as modifying insulin dosages or introducing new medications, to ensure that the individual's diabetes management remains effective throughout the honeymoon phase and beyond.
Understanding the duration and variability of the honeymoon phase is crucial for individuals living with Type 1 diabetes and their healthcare teams. It highlights the importance of personalized management plans and ongoing support to navigate this period effectively. As the honeymoon phase progresses, individuals may require more frequent insulin adjustments and closer monitoring to prevent complications associated with fluctuating blood glucose levels.
The Honeymooners: A Cinematic Journey Through Love and Laughter
You may want to see also

Insulin Production: It involves a temporary increase in insulin production by the pancreas
The honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes refers to a period of time, often lasting a few weeks to a few months after diagnosis, during which individuals may experience a temporary improvement in their blood sugar control without the need for insulin injections. This phenomenon is an intriguing aspect of the disease, as it presents a unique challenge for healthcare professionals and researchers. During this phase, the pancreas seems to compensate for the loss of insulin production by increasing its own insulin output, leading to better glucose management.
This temporary increase in insulin production is a complex physiological response. When a person is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, their immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. As a result, the pancreas initially compensates by producing more insulin to try and maintain normal blood sugar levels. This surge in insulin production is a natural reaction to the body's attempt to restore balance.
The duration of this honeymoon phase can vary widely among individuals. Some people may experience it for a few weeks, while others might have it last for several months. It is essential to understand that this phase is not a permanent solution to managing diabetes. As the disease progresses, the pancreas's ability to produce excess insulin diminishes, and individuals typically transition into a phase where they require insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
During this time, it is crucial for individuals to closely monitor their blood glucose levels and work closely with healthcare providers. The increased insulin production can lead to lower blood sugar levels, which may require adjustments in medication and lifestyle to prevent hypoglycemia. Healthcare professionals often use this period to educate patients about the importance of long-term diabetes management and to establish a personalized treatment plan.
Understanding the honeymoon phase provides valuable insights into the complex nature of type 1 diabetes. It highlights the body's initial response to the disease and the need for tailored medical care. While this phase offers a temporary respite from insulin injections, it is a critical period for individuals to learn about their condition and prepare for the long-term management of diabetes.
Volcano's Fury: American Honeymooners' Escape from Disaster
You may want to see also

Blood Sugar Control: Improved blood sugar control is a key characteristic during this period
The honeymoon phase in Type 1 diabetes is a period of time, often lasting a few weeks to a few months, during which newly diagnosed individuals may experience a natural improvement in blood sugar control. This phenomenon is an intriguing aspect of the disease, as it provides a temporary respite from the constant monitoring and management that Type 1 diabetes typically requires. During this phase, the body's immune system may take a break from attacking the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, allowing for better insulin production and utilization. As a result, individuals may notice a reduction in their blood glucose levels and a decrease in the frequency of hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) episodes.
Improved blood sugar control is a key characteristic of this phase, and it can significantly impact the overall management of the condition. For many people, this period offers a chance to adjust their diabetes management strategies and potentially reduce the amount of insulin they need to inject or the frequency of blood glucose tests. It is a time when individuals can reassess their dietary habits, exercise routines, and medication regimens to optimize their blood sugar levels. Healthcare providers often use this time to educate patients on the importance of consistent monitoring and the potential need for long-term lifestyle modifications.
During the honeymoon phase, the body's insulin production may increase, leading to better glucose uptake by cells and improved insulin sensitivity. This enhanced insulin sensitivity allows the body to use the available insulin more efficiently, resulting in lower blood sugar levels. As a result, individuals may feel more energetic and experience a reduction in the symptoms associated with high blood glucose, such as frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue. However, it is crucial to remember that this improvement is temporary and may not last indefinitely.
It is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes to be aware of the potential risks and challenges that may arise during the honeymoon phase. While improved blood sugar control is beneficial, it can also lead to a false sense of security, causing some patients to become less diligent in their diabetes management. This may result in a dangerous situation where blood glucose levels become too low, leading to hypoglycemia. Therefore, individuals should continue to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and maintain a consistent diabetes management routine to ensure long-term health and well-being.
In summary, the honeymoon phase in Type 1 diabetes is a critical period that offers improved blood sugar control, providing a temporary break from the rigorous management required for this condition. It is a time for individuals to reassess their diabetes care and make necessary adjustments. However, it is crucial to remain vigilant and continue following a comprehensive diabetes management plan to prevent complications and maintain optimal health. Understanding and recognizing the characteristics of this phase can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their diabetes care.
Paris: The Ultimate Romantic Getaway for a Memorable Honeymoon
You may want to see also

Lifestyle Factors: Diet, exercise, and stress management can influence honeymoon phase duration
The honeymoon phase, a period of time after diagnosis when many individuals with type 1 diabetes experience improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin requirements, can vary significantly in its duration. While some people may enjoy this phase for several months, for others, it might last only a few weeks. Understanding the factors that can influence the length of this phase is crucial for effective diabetes management.
Lifestyle factors play a pivotal role in determining how long the honeymoon phase lasts. One of the most significant is diet. Maintaining a balanced diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables is essential. This type of diet helps stabilize blood sugar levels, which can extend the honeymoon phase. For instance, foods with a low glycemic index (GI) release glucose slowly into the bloodstream, providing more stable energy and potentially delaying the need for increased insulin. Conversely, a diet high in simple sugars and refined carbohydrates can lead to rapid spikes in blood glucose, potentially shortening the honeymoon period.
Regular exercise is another critical component. Physical activity helps the body use insulin more efficiently, which can reduce the need for insulin injections during the honeymoon phase. Aerobic exercises, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, are particularly beneficial as they can lower blood sugar levels and improve overall insulin sensitivity. Strength training exercises also play a role, as they can increase muscle mass, which further enhances insulin sensitivity. However, it's important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to ensure they remain within a safe range.
Stress management is often overlooked but can significantly impact blood sugar levels and, consequently, the duration of the honeymoon phase. When stressed, the body releases hormones that can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Chronic stress can lead to prolonged periods of elevated blood glucose, potentially shortening the honeymoon phase. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or even engaging in hobbies and social activities can help manage stress. These activities promote relaxation and can contribute to a more stable blood sugar environment, thereby extending the honeymoon phase.
In summary, the honeymoon phase in type 1 diabetes can be influenced by several lifestyle factors. Adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and implementing effective stress management techniques can all contribute to extending this phase. By understanding and managing these factors, individuals with type 1 diabetes can potentially enjoy a longer period of improved blood sugar control and reduced insulin needs.
Frankie Avalon's Unseen Role in The Honeymooners
You may want to see also

Individual Variability: Each person's honeymoon phase may differ in length and intensity
The concept of a "honeymoon phase" in Type 1 diabetes refers to a period of time, often lasting a few weeks to a few months after diagnosis, during which some individuals experience a temporary improvement in their blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. This phenomenon can be attributed to the body's natural response to the recent diagnosis, where the pancreas may still be producing some insulin, and the body is adjusting to the new condition. However, it's important to note that this honeymoon phase is not a universal experience and can vary significantly from person to person.
Individual variability in the honeymoon phase is a critical aspect of understanding Type 1 diabetes management. The duration and intensity of this phase can differ widely, and several factors contribute to these variations. Firstly, the timing of diagnosis plays a crucial role. Individuals diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes at an early age might experience a longer honeymoon phase as their bodies have more time to adapt. Conversely, those diagnosed at a more advanced stage may have a shorter or less pronounced honeymoon period. The body's natural response to the disease is another factor; some individuals' immune systems may take longer to attack the pancreas, leading to a prolonged honeymoon phase.
Genetic predisposition also influences the length and intensity of the honeymoon phase. Research suggests that certain genetic variations can affect the rate at which the pancreas is destroyed and the body's response to insulin. Individuals with a family history of Type 1 diabetes might have a different experience compared to those without such a history. Additionally, the presence of other autoimmune conditions can impact the honeymoon phase. If a person has multiple autoimmune disorders, their body's immune response may be more aggressive, potentially shortening the honeymoon period.
Environmental and lifestyle factors also contribute to individual differences. Diet, exercise, and overall health can influence how the body manages blood sugar levels. For instance, a person with a healthier lifestyle and better dietary habits might experience a longer and more beneficial honeymoon phase. Conversely, those with less control over their diet and lifestyle may see a shorter or less effective honeymoon period. Furthermore, the level of support and education received after diagnosis can impact an individual's ability to manage their diabetes effectively during this phase.
Understanding these individual variations is essential for healthcare providers and diabetes management teams. It allows for more personalized treatment plans and education, ensuring that patients receive the appropriate support during and after the honeymoon phase. Recognizing that each person's experience is unique can help in setting realistic expectations and goals for diabetes management, ultimately improving the overall quality of life for individuals living with Type 1 diabetes.
Honeymoon Budget: Finding the Perfect Balance for Your Dream Getaway
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The honeymoon phase refers to a period after a person is diagnosed with type 1 diabetes when their blood sugar levels may improve, and they might experience a temporary reduction in insulin requirements. This phenomenon is often observed in the early stages of diagnosis.
The duration of the honeymoon phase can vary widely among individuals. It may last for a few weeks, months, or even a year or more. Some people might experience it for a shorter period, while others may have a more prolonged and significant improvement in their blood sugar control.
Yes, the honeymoon phase can impact diabetes management. During this time, individuals might find that their blood glucose levels are easier to control, and they may require lower doses of insulin. However, it's essential to remain vigilant and continue monitoring blood sugar levels to ensure they stay within a healthy range.
Several factors can influence the duration and intensity of the honeymoon phase. These include the individual's overall health, the timing of diabetes diagnosis, the presence of any complications, and the body's response to insulin therapy. Additionally, lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and stress levels can also play a role.
Effective diabetes management during and after the honeymoon phase involves regular blood glucose monitoring, maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to prescribed insulin therapy. It is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to adjust treatment plans as needed and ensure optimal blood sugar control.







